Are You a Healthcare Professional?
This European website, initiated and developed by CSL Behring, has two separate sections with the aim to provide information on haemophilia for an international audience, either to European healthcare professionals or to the general public.*
Yes, I am a healthcare professional*
No, I am not a healthcare professional
Haemophilia Treatment Today

Haemophilia Treatments
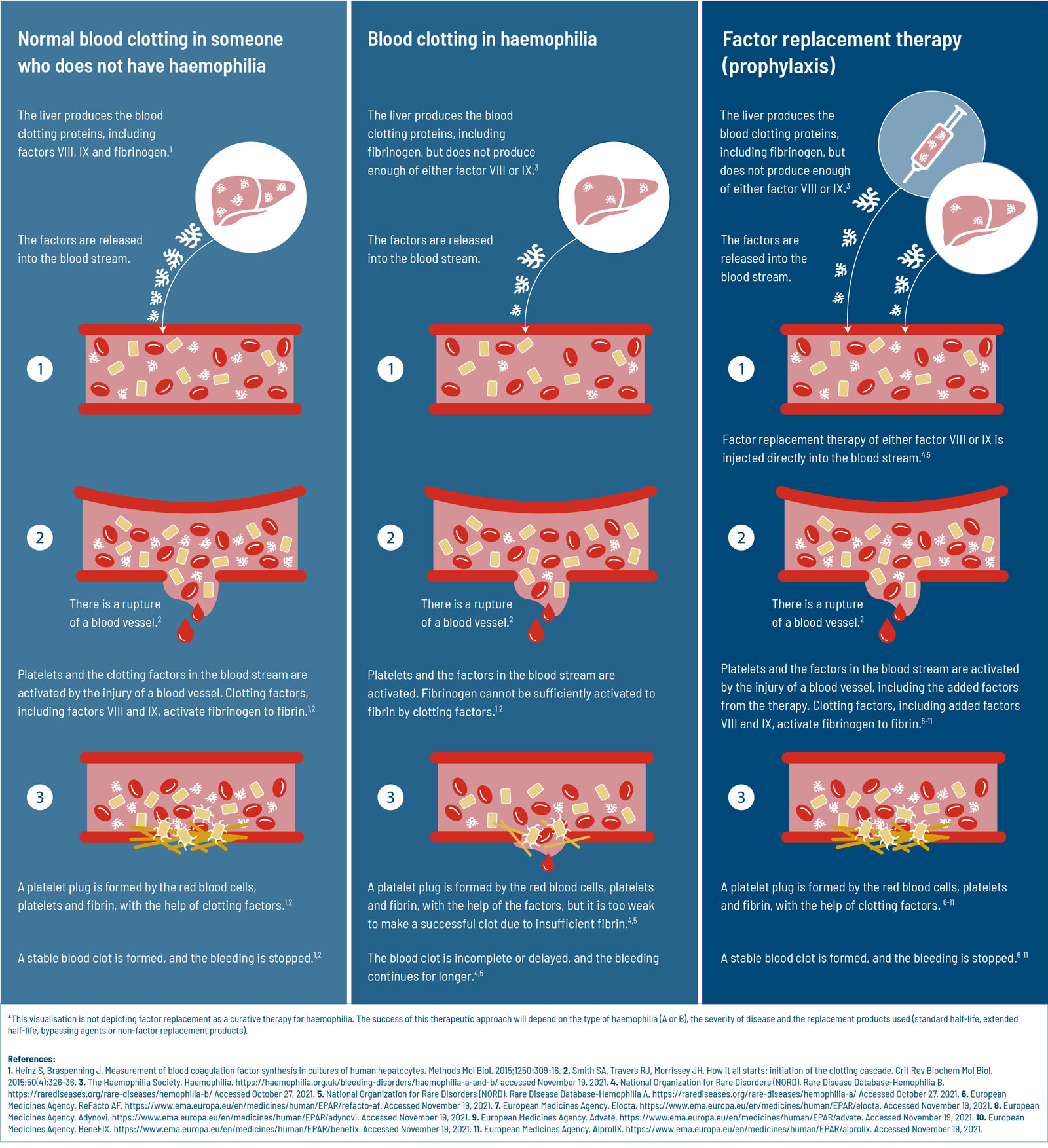
Many people with haemophilia require regular intravenous infusions of factor replacement.1 This is because people with moderate to severe haemophilia have less than 1% to 5% of factor levels compared with 40% to 150% for people without haemophilia.4-7 To maintain near normal factor levels, people with haemophilia require infusions with replacement factors. Depending on factor levels, some require intravenous infusions as often as every other day.1
Therapies for haemophilia have been continuously improving, becoming more effective at controlling symptoms while reducing the frequency of treatment. For example, extended half-life (EHL) products have been introduced, which require fewer infusions.1
CURRENTLY AVAILABLE TREATMENT OPTIONS

Do you know?
How Haemophilia Treatments Work
Replacement Clotting Factors: How Do They Work?
People without haemophilia have clotting factors at a level of 40% to 150%. That is far greater than people with moderate (1-5%) or severe (less than 1%) haemophilia.4-7 To make sure people with haemophilia have enough clotting factors to prevent bleeds, those with haemophilia A receive regular infusion of functional clotting factor VIII6 and for haemophilia B, factor IX.5
The clotting factors are produced by cells in the liver.17 When people with haemophilia receive factor replacement therapy, they are essentially bypassing their liver, by adding clotting factor directly into the bloodstream. This means that they have the ability to form blood clots,5,6 but without help from the liver. The only way to maintain the ability to clot is to continuously add more clotting factor to the blood stream. Unfortunately, clotting factors do not last very long. These factor proteins deplete every 8-12 hours (factor VIII)18 or 18-24 hours (factor IX).1 This is why liver cells are continuously producing more clotting factors and why people with haemophilia need to receive replacement factors so frequently. The treatment schedule of receiving replacement factors depends on both the type of haemophilia (A or B) and the severity of haemophilia (natural factor levels).5,6
TREATMENT DEVELOPMENT
Today There is Access to a Larger Variety of Treatments and More are in Development2,3
Some people may remember or are aware of the limited options people with haemophilia had only decades ago. Until the mid-1960s, when Dr. Judith Pool figured out how to combine clotting factors from multiple blood donations, the average life expectancy for haemophilia was only 12 years of age.5
Since that time, treatment has been revolutionised.1 Today, people with haemophilia are not reliant on blood donations5,14 and extended half-life products allow for more freedom and flexibility in treatment schedules.18,19 Even though treatment has come a long way, novel treatment strategies are still being developed today2,3 with the goal of improving lives even more.20
Haemophilia Treatment Through Time
Prior to the modern era of haemophilia, no reliable treatments existed. Instead, people with haemophilia were given whole blood infusions which did not have enough factor replacement during bleeding episodes. Fortunately, little by little, treatments have advanced to where most individuals with haemophilia lead more free and active lives.5
1964
Method for Isolating Clotting Factors Discovered
Dr. Judith Pool discovered that factor VIII, which is damaged in haemophilia A, is the last component of plasma to thaw after freezing. This breakthrough allowed for clotting factors from multiple donors to be isolated and combined so higher concentrations of clotting factors could be transfused.21 As a consequence, life expectancy increased from 12 to 24 years of age.14
1960s-1970s
Development of Stable, Concentrated Formations of Clotting Factors
A method was developed to produce concentrated clotting factors as a powder. Now, people with haemophilia could store their medication and administer clotting factors at home, reducing the number of weekly trips to the hospital.5,11
1970s - 1980s
A Dark Period for Haemophilia: The Blood Supply is Contaminated
Beginning in early 1970, many individuals were exposed to hepatitis after receiving factor concentrate transfusions.5,22 In early 1980s, HIV was found in the blood supply,5,15 ultimately 40% of Americans with haemophilia died of complications related with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).15
1992 - 1999
The EMA and FDA Approve the First Engineered Recombinant Factor Product
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) and United States (US) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first genetically engineered factor IX (1997; 1997) and later factor VIII (1999; 1992) replacement therapy, respectively.5,12,13
2014 - 2016
2011 - 2017
Trials of First Gene Therapy Products Begin
In 2011, results from the first clinical trial for a factor 9 gene therapy and in 2017, for a factor 8 gene therapy were released.3,16
2022-PRESENT
First Gene Therapies for Haemophilia Approved in Europe and in the USA
In 2022 and 2023, the first adeno-associated virus vector-based gene therapies for the treatment of adults with haemophilia A and B were approved in Europe and in the USA.25,26,27

Previous
Living with Haemophilia Today
Recent scientific advancements have revolutionized available treatments and more can be done to ensure patients are living the highest quality life.
Next
Gene Therapy
Discover the advances scientists have made over the last 50 years, making genetic therapies possible for many patients with genetic diseases and chronic conditions.
References
- Srivastava A, Santagostino E, Dougall A, et al. WFH guideline for the management of hemophilia, 3rd edition. Haemophilia. 2020;00:1-158.
- Nathwani AC, Reiss UM, Tuddenham EGD, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of factor IX gene therapy in hemophilia B. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1994-2004.
- Rangarajan S, Walsh L, Lester W, et al. AAV5-Factor VIII gene transfer in severe hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(26):2519-2530.
- Berntorp E, Fischer K, Hart DP, et al. Haemophilia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:45.
- National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD). Rare Disease Database-Hemophilia B. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/hemophilia-b/ Accessed October 27, 2021.
- National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD). Rare Disease Database-Hemophilia A. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/hemophilia-a/ Accessed October 27, 2021.
- Mehta P, Reddivari AKR. Hemophilia. [Updated 2023 Jun 5]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551607/
- Mancuso ME, Santagostino E. Outcome of clinical trials with new extended half-life FVIII/IX concentrates. J Clin Med. 2017;6,39.
- High KA, Roncarolo MG. Gene therapy. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(5):455-464.
- McCain J. The future of gene therapy. Biotechnol Healthc. 2005;2(3):52-54,56-60.
- Morfini M. The history of clotting factor concentrates pharmacokinetics. J Clin Med. 2017;6,35.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). BeneFIX. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/benefix. Accessed November 30, 2021.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). ReFacto AF. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/refacto-af. Accessed November 30, 2021.
- Hemophilia Federation of America (HFA). Bleeding Disorders Historical Timeline. https://www.hemophiliafed.org/history-of-bleeding-disorders/. Accessed July 14, 2023.
- White GC. Hemophilia: an amazing 35-year journey from the depths of HIV to the threshold of cure. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2010;121:61-73; discussion 74-5. PMID: 20697550; PMCID: PMC2917149.
- Nathwani AC, Tuddenham EGD, Rangarajan S, et al. Adenovirus-associated virus vector-mediated gene transfer in hemophilia B. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(25):2357-2365.
- Heinz S, Braspenning J. Measurement of blood coagulation factor synthesis in cultures of human hepatocytes. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1250:309-16.
- Ay C, Feistritzer C, Rettl J, et al. Bleeding outcomes and factor utilization after switching to an extended half-life product for prophylaxis in haemophilia A in Austria. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):12967.
- Chhabra A, Spurden D, Fogarty PF, et al. Real-world outcomes associated with standard half-life and extended half-life factor replacement products for treatment of haemophilia A and B. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2020;31(3):186-192.
- Perrin GQ, Herzog RW, Markusic DM. Update on clinical gene therapy for hemophilia. Blood. 2019;133(5):407-414.
- Pool JG, Hershgold EJ, Pappenhagen AR. High-potency antihaemophilic factor concentrate prepared from cryoglobulin precipitate. Nature. 1964;203:312.
- Kasper CK, Kipnis SA. Hepatitis and clotting-factor concentrates. JAMA 1972;221(5):510.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Elocta. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/elocta. Accessed October 30, 2021.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Alprolix. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/alprolix. Accessed October 30, 2021.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Roctavian. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/roctavian-0. Accessed January 28, 2023.
- Food and Drug Administration. Approved Cellular and Gene Therapy Products. https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/cellular-gene-therapy-products/approved-cellular-and-gene-therapy-products. Accessed September 5, 2023.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Hemgenix. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/hemgenix. Accessed January 28, 2023.